Spring Security OAuth2.0 파헤치기! - 1(Authorization Server)

내부 챗봇 솔루션을 개발하면서, OAuth2.0을 이용하여 자체 인증서버를 구축할 일이 생겼다. 최근에 웹 또는 앱을 보면서 자주 접하게 되는 인증 방식이 OAuth2.0 방식이다. 대표적으로 네아로(네이버 아이디로 로그인), 페이스북으로 로그인, 구글아이디로 로그인 등등이 지금부터 설명하게 될 OAuth2.0 인증방식이다. 그렇다면 왜 OAuth2.0을 사용하게 되었을까? 사실 많은 이유가 있겠지만 페이스북을 예제로 보면 3rd-party 애플리케이션이 페이스북의 특정 기능(3rd-party 애플리케이션 사용자의 리소스)을 사용하게 되면 사용자의 동의를 받아야한다.그러면 사용자의 페이스북 인증정보를 3rd-party 애플리케이션에도 가지고 있어야할까? 아니다 ! 인증은 페이스북에서 하는 것이고 3rd-party 애플리케이션은 페이스북에게 접근을 허가할 액세스 토큰을 발급받고 그 토큰으로 사용자의 리소스를 페이스북에게 요청하여 사용하는 것이다. 이런저런 이유로 각광받고 있는 OAuth2.0이다. 제 3자에게 인증을 받는다? 정말 특이한 놈이다. 물론 OAuth2.0이 완벽하고 빈틈없는 인증방식은 아닐 것이다. 무조건 믿고 사용하는 것은 일을 그릇칠 수 있기에 OAuth2.0을 포함하여 많은 보안취약점을 보완해야 할것같다. 우선 예제 코드를 짜기에 앞서 OAuth2.0의 용어를 짚고 넘어가야 한다.
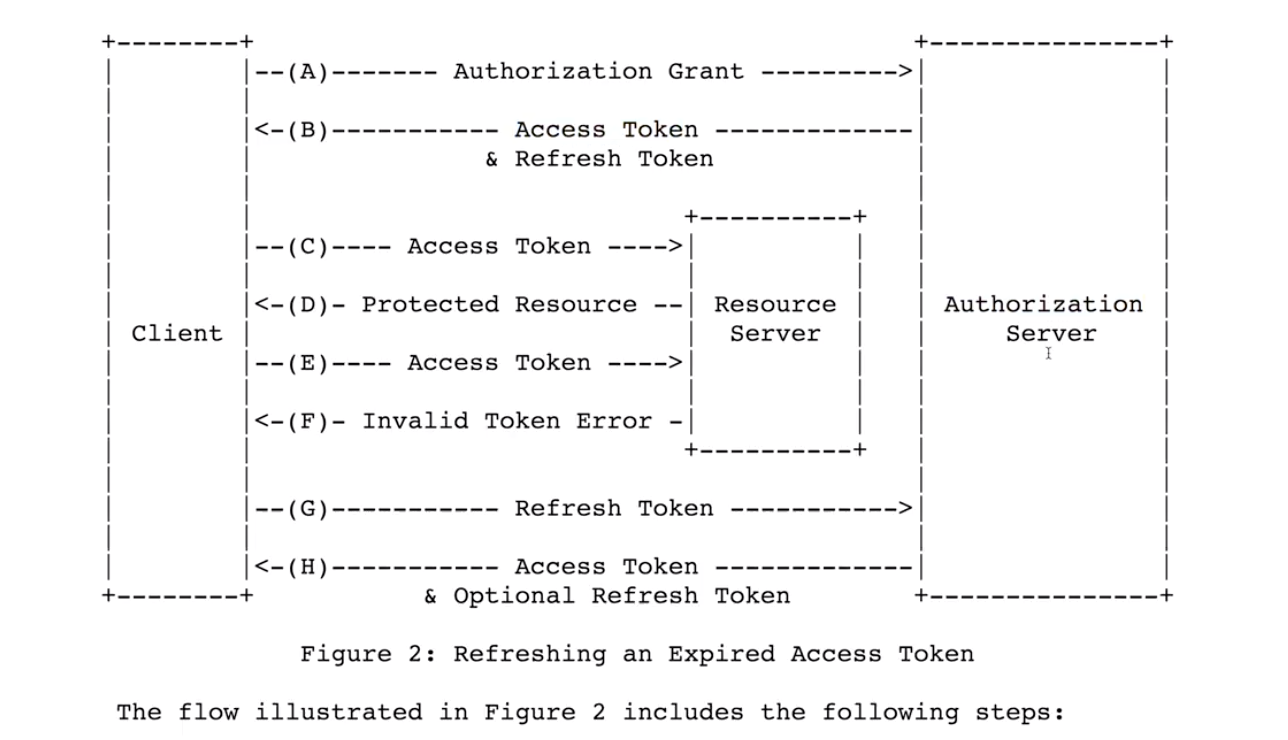
위 그림은 RFC6749 표준 문서에 나와있는 그림이다.(https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749)
RFC 6749 - The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework
[Docs] [txt|pdf] [draft-ietf-oaut...] [Tracker] [Diff1] [Diff2] [IPR] [Errata] Updated by: 8252 PROPOSED STANDARD Errata Exist Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) D. Hardt, Ed. Request for Comments: 6749 Microsoft Obsoletes: 5849 October 2012 Category:
tools.ietf.org
지금 설명할 서로 각자의 Role이 있는 주체들의 인증,인가 흐름이다.
필자가 생각한 용어 설명
- Resource Owner(자원소유자) : 자신의 리소스를 사용할 수 있게 Third-party Application(인증 서버 입장에서 Client Application)에게 사용을 허가하는 Third-party Application 사용자.
- Resource Server(리소스 서버) : Resource Owner의 리소스를 가지고 있으며, 해당 리소스를 보호하는 Application. Client Application은 Authorization Server에게 발급받은 토큰을 이용하여 Resource Server에게 사용자 리소스를 받아 사용한다.
- Authorization Server(인증서버) : Client Application이 Resource Owner의 리소스를 사용하기 위하여 Client Application에게 인가(토큰발급)해주는 역할을 하는 Application.
- Client(클라이언트 애플리케이션) : Resource Server에 유지되고 보호되고 있는 Resource Owner의 리소스를 사용하는 Application. Authorization Server에게 적절한 인증을 통하여 토큰을 발급받고 해당 토큰을 이용해 Resource Server에서 보호된 Resource Owner의 리소스를 사용한다. 이 Application은 실제로 Resource Owner가 접속하여 사용중인 Application이며, 단순 Javascript Application 일수도 있고, Server로 기동되고 있는 Application일수도 있다.
사실 처음 용어를 접하게 되면 이해가 힘든 부분들이 있다. Client? 우리가 생각하는 Client는 사용자 인데, OAuth2.0에서는 어떠한 애플리케이션이다. 물론 잘생각하면 Client가 맞다. 왜냐하면 Resource Server 입장에서 Third-party Application은 클라이언트니까.. 뭐 최대한 이해를 돕기 위하여 나름 고심해서 내린 용어 설명이다.
RFC6749에 명시된 용어설명
- Resource Owner(자원소유자) : 보호된 자원에 대한 액세스 권한을 부여할 수 있는 엔티티. 리소스 소유자가 사람인 경우 리소스 소유자는 최종 사용자.
- Resource Server(리소스 서버) : 보호된 자원을 호스팅하는 서버. 액세스 토큰을 사용하여 보호된 리소스 요청에 응답.
- Client(클라이언트) : 애플리케이션을 대신하여 보호된 리소스 요청을 하는 애플리케이션. 응용 프로그램 서버, 데스크톱 등이 될 수 있다.
- Authorization Server(권한 서버) : 클라이언트에게 액세스 토큰을 발급하는 서버. 자원 소유자를 인증하고 리소스 접근 권한을 클라이언트에게 임명한다.
다음은 OAuth2.0에서 사용하는 인증 Grant Type이다. 인증 Grant Type이란 Client가 액세스토큰을 발급받기 위한 플로우라고 보면 된다. 총 4개의 Grant Type이 있다.(사실 Refresh_token이라는 Grant Type도 있지만, 인증 Grant Type으로 넣어야하나 애매한 부분이 있다.)
- Authorization Code Grant : OAuth2.0 Grant Type에서 가장 잘 알려진 인가 코드 그랜트 타입은 중요한 보안 이점을 제공하는 방법이다. 클라이언트는 토큰을 발급 받기 전에 인증코드라는 것을 사전에 리소스 소유자에 의해서 받게 되고 그 인증코드(권한 부여코드)를 가지고 인증서버에 요청을 보내야 토큰을 발급받을 수 있다.
- Implicit Grant : 암시적 그랜트 타입은 서버가 없는 단순 웹 브라우저에서 직접 실행되는 자바스크립트 웹 애플리케이션 클라이언트에게 적당한 권한 부여 방법이다. 별다른 인증방법없이 클라이언트가 요청을 보내면 리소스 소유자의 Authentication(+사용자 동의 과정) 과정만 거치고 바로 토큰을 발급해준다. 이 그랜트 타입은 클라이언트가 토큰을 안전하게 보관할 방법이 없기때문에 리프레시 토큰을 발급해주지 않는다.
- Resource Owner Password Credentials : 사용자 패스워드 자격증이다. 이 그랜트 타입은 클라이언트와 OAuth프로바이더(Resource Server + Authorization Server)가 전혀다른 애플리케이션일때는 이 그랜트 타입이 사용자의 자격증명 정보를 요구하기 때문에 가능하면 사용하지 않는 것이 좋다. 하지만 클라이언트와 OAuth2.0 프로바이더(간단히 Resource Server+Authorization Server)가 동일한 솔루션에 속할 때는 안전하게 사용될 수도 있다. 그리고 반드시 입력받은 리소스 소유자의 자격증명 정보는 보관하지 않고 즉시 폐기해야한다.
- Client Credentials Grant : 애플리케이션이 리소스 소유자의 리소스 대신 자체적인 리소스에 대한 접근이 필요할 때 사용할 수 있는 그랜트 타입이다. 이전에는 서드파티 애플리케이션이 리소스 소유자 대신 리소스 소유자의 리소스에 접근하는 형태였지만, 클라이언트 자격증명 그랜트 타입은 인증서버에 등록된 클라이언트이기만 하면 리소스에 접근할 수 있는 특별한 형태의 그랜트 타입이다. 또한 사용자와의 연관이 존재하지 않기 때문에 리프레시 토큰을 발급하지 않는다. 토큰이 만료되면 자체적으로 새로운 액세스 토큰을 발급받는다.




위에 설명한 Grant Type의 플로우가 담긴 그림들이다.
여기까지 OAuth2.0의 용어 설명이다. 부족한 것이 있거나 이해가 안되는 부분이 있다면 구글링을 통해 용어를 정확하게 다시 이해하고 오는 것이 좋겠다.
대부분 OAuth2.0에 관련된 글들은 Resource Server와 Authorization Server의 구분이 없는 글들이 많다. 네이버에 계신 어느 개발자님에 따르면 구현 자체도 애매모호하게 되어 있는 부분도 없지않아 있고, 레퍼런스도 불친절하게 나와있는 탓에 둘을 구분하여 개발하기 힘든 이유도 있다고한다. 하지만 필자는 완벽하고 100% 맞다고 확신하지는 않지만 소스코드를 분석하고 예제를 짜면서 조금 얻은 지식으로 Resource Server, Authorization Server, Client를 나누어서 개발할 것이다. 혹시나 잘못된 부분, 부족한 부분이 있다면 코멘트 남겨주길 간곡히 부탁한다.
오늘 예제는 모두 In-Memory가 아닌 DB를 이용한 데이터 관리를 할 것이다. 예제를 진행하기 앞서 필요한 DB 스키마를 정리해보았다. Spring Security에서 제공한 DB 스키마도 있지만 조금 다른 부분도 있다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
|
-- 클라이언트 등록과 관련된 데이터 테이블
create table oauth_client_details (
client_id VARCHAR(256) PRIMARY KEY,
resource_ids VARCHAR(256),
client_secret VARCHAR(256),
scope VARCHAR(256),
authorized_grant_types VARCHAR(256),
web_server_redirect_uri VARCHAR(256),
authorities VARCHAR(256),
access_token_validity INTEGER,
refresh_token_validity INTEGER,
additional_information VARCHAR(2000),
autoapprove VARCHAR(256)
);
-- 발급된 액세스 토큰을 저장하기 위한 테이블
-- 예제는 JWT 토큰을 사용하므로 사용하지 않는다. 하지만 JWT토큰을 사용하지 않으면 해당 스키마를 사용한다.
create table oauth_access_token (
token_id VARCHAR(256),
token clob,
authentication_id VARCHAR(256) PRIMARY KEY,
user_name VARCHAR(256),
client_id VARCHAR(256),
authentication clob,
refresh_token VARCHAR(256)
);
-- 리프레시 토큰 발급을 위한 테이블
-- 이 테이블도 역시 JWT 토큰을 사용하므로 사용하지 않는다.
create table oauth_refresh_token (
token_id VARCHAR(256),
token varchar(1000),
authentication varchar(1000)
);
-- 사용자(Resource Owner)의 승인을 저장하기 위한 테이블
create table oauth_approvals (
userId VARCHAR(256),
clientId VARCHAR(256),
scope VARCHAR(256),
status VARCHAR(10),
expiresAt TIMESTAMP,
lastModifiedAt TIMESTAMP
);
-- authorization code table
create table oauth_code (
code VARCHAR(256), authentication blob
);
|
cs |
이번 예제에 필요한 부분도 있고 필요하지 않은 부분도 있기에 예제에서 스키마에 대한 설명을 진행하도록 하겠다.
첫번째 구현할 것은 Authorization Server이다. 인증 서버는 클라이언트 애플리케이션에게 액세스토큰,리프레시 토큰 등을 발급해주는 역할을 하는 서버이다. 물론 토큰 발급 이전에 선행되는 Resource Owner의 인증과정이 포함되어있다. 그리고 Spring security OAuth2.0은 Spring Security와 상호보완적이다. 즉, Spring Security에서 하던 코딩도 어느정도 들어가야한다. 혹시 Spring Security를 잘모른다면 선행해서 봐야할 것 같다. 아래 링크에서 Spring Security를 참고하면 될듯하다. 바로 예제 소스로 들어가겠다.
https://coding-start.tistory.com/153
Spring boot - Spring Security(스프링 시큐리티) 란? 완전 해결!
오늘 포스팅할 내용은 Spring Security이다. 사실 필자는 머리가 나빠서 그런지 모르겠지만, 아무리 구글링을 통해 스프링 시큐리티를 검색해도 이렇다할 명쾌한 해답을 얻지 못했다. 대부분 이론적인 설명들은..
coding-start.tistory.com
필요한 DB스키마를 생성해준다. 위의 스키마 중에 OAUTH_CLIENT_DETAILS, OAUTH_APPROVALS, OAUTH_CODE 테이블을 생성해준다.
- OAUTH_CLIENT_DETAILS : 인증서버가 토큰을 발급해줄때, 등록된 유효한 클라이언트 애플리케이션이 맞는지 확인할때 사용되는 테이블이다.
- OAUTH_APPROVALS : Resource Owner가 3rd-party 애플리케이션을 사용할때 마다, 해당 애플리케이션이 사용자의 리소스에 접근하는 것을 허락하겠냐라는 문구를 항상 띄워 줄수는 없을 것이다. 즉, 해당 테이블에는 최초로 Resource Owner가 3rd-party 애플리케이션에게 자신의 리소스 사용을 허락할때 Approval했다라는 데이터를 삽입한다. 그 이후로는 더 이상 Resource Owner에게 Approval 관련된 문구(팝업 등)을 띄우지 않을 것이다.
- OAUTH_CODE : 오늘 진행해볼 Authorization Code Grant Type에 사용될 인증코드를 보관하는 테이블이다.
pom.xml
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>oauth_authorization_server</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>oauth_authorization_server</name>
<description>spring security exam</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<repositories>
<!-- 오라클 저장소 -->
<repository>
<id>codelds</id>
<url>https://code.lds.org/nexus/content/groups/main-repo</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>bootstrap</artifactId>
<version>3.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ucp</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
cs |
필요한 라이브러리들을 받아준다. 사용되는 라이브러리들 중에 롬복을 설치하지 않은 사람이 있다면 이전 포스팅에 롬복 설치방법에 대한 글을 올린 것을 참조하길 바란다.
https://coding-start.tistory.com/78?category=738632
Mac OS - Eclipse & Lombok(롬복 사용방법)
해당 환경은 모두 Mac OS환경에서 진행되었습니다. Lombok(jar) 설치 https://projectlombok.org/download에서 최신버전 혹은 원하는 버젼의 Lombok을 다운로드 받아 줍니다. Lombok jar 실행 lombok이 설치된 경..
coding-start.tistory.com
application.properties
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
spring.application.name=oauth2_authorization_server
server.port=8080
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
############################<DataSource&JPA>###############################
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:59162:XE
spring.datasource.username=oauth_user
spring.datasource.password=oauth_user
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
spring.datasource.tomcat.initial-size=0
spring.datasource.tomcat.max-active=50
spring.datasource.tomcat.max-wait=10000
spring.datasource.tomcat.max-idle=0
spring.datasource.tomcat.min-idle=0
spring.datasource.tomcat.remove-abandoned=true
spring.datasource.tomcat.remove-abandoned-timeout=10000
spring.datasource.tomcat.validation-interval=10000
spring.datasource.tomcat.validation-query-timeout=10000
spring.datasource.tomcat.validation-query=SELECT 1 FROM dual
spring.datasource.tomcat.test-on-borrow=true
spring.datasource.tomcat.test-on-connect=true
spring.datasource.tomcat.test-on-return=true
spring.jpa.showSql=true
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=false
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy=org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql=false
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.default_schema=oauth_user
############################</DataSource&JPA>#############################
|
cs |
많지 않은 설정이다. DataSource, JPA 설정이 대부분이다. OAuth2.0에 관련된 대부분의 설정은 모두 Java Config 기반이다.
OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfig.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
|
/**
*
* @author yun-yeoseong
*
*/
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfig extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter{
@Autowired private DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired private PasswordEncoder encoder;
@Autowired private ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService;
@Autowired private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) throws Exception {
}
/*
* Client에 대한 인증 처리를 위한 설정
* 1) In-Memory 설정 - 기본 구현체 InMemoryClientDetailsService(Map에 클라이언트를 저장)
* 2) JDBC 설정 - 기본 구현체 JdbcClientDetailsService(JdbcTemplate를 이용한 DB이용)
* 3) CleintDetailsService 설정
*/
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
/*
* Client를 DB에서 관리하기 위하여 DataSource 주입.
* UserDetailsService와 동일한 역할을 하는 객체이다.
*/
clients.withClientDetails(clientDetailsService);
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
endpoints
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService) //refresh token 발급을 위해서는 UserDetailsService(AuthenticationManager authenticate()에서 사용)필요
.authorizationCodeServices(new JdbcAuthorizationCodeServices(dataSource)) //authorization code를 DB로 관리 코드 테이블의 authentication은 blob데이터타입으로..
.approvalStore(approvalStore()) //리소스 소유자의 승인을 추가, 검색, 취소하기 위한 메소드를 정의
.tokenStore(tokenStore()) //토큰과 관련된 인증 데이터를 저장, 검색, 제거, 읽기를 정의
.accessTokenConverter(accessTokenConverter())
;
}
@Bean
public JwtTokenStore tokenStore() {
return new JwtTokenStore(accessTokenConverter());
}
@Bean
public JdbcApprovalStore approvalStore() {
return new JdbcApprovalStore(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter accessTokenConverter() {
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey("non-prod-signature");
return converter;
}
/*
* 새로운 클라이언트 등록을 위한 빈
*/
@Bean
public ClientRegistrationService clientRegistrationService() {
return new JdbcClientDetailsService(dataSource);
}
}
|
cs |
Authorization Server 관련 설정 Java class이다. 우선 @Configuration, @EnableAuthorizationServer 어노테이션을 붙여 해당 프로젝트가 인증서버임을 알린다. 그리고 해당 클래스는 AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter를 상속받는다. 첫번째 AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer를 매개변수로 가진 설정 메소드이다. 해당 메소드에서 설정하는 것은 AuthenticationEntryPoint, AccessDeniedHandler, PasswordEncoder 등을 설정할 수 있는 메소드이다. 몇 개 테스트를 해보니 여기에 아무리 설정을 하여도 Spring Security 설정 클래스에 적용된 AuthenticationEntryPoint, AccessDeniedHandler, PasswordEncoder등을 사용한다. 즉, Spring Security와 상호보완적이라고 표현한 것을 이것을 생각하여 말한것이다. 두번째는 ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer 매개변수를 가진 메소드이다. 쉽게 설명하면 Client관련된 동작들을 Im-memory에서 할 것인지 Jdbc를 이용해서 할것인지에 대한 설정이라고 보면된다. Client 애플리케이션 관리를 인메모리에서 하는 것은 말도 안되므로, jdbc를 이용한 클라이언트 관리 설정을 해주었다. DB를 이용하여 클라이언트를 관리하는 설정에는 크게 두가지 방법이있다.
위처럼 직접 DB와 통신하게 되는 ClientDetailsService 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스를 등록하는 방법이 있고, 나머지 하나는 OAuth2.0에서 제공하는 JdbcClientDetailsService를 사용하기위해 DataSource를 설정해주는 방법이다.( -> clients.jdbc(dataSource) )
마지막으로 가장 중요한 AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer를 매개변수로 가진 메소드이다. 사실 이 설정이 Authorization Server의 설정의 전부라고 해도 무방할정도로 중요한 설정 메소드이다. 이 설정은 Authorize, Token 발급, Token Check할때의 행동을 정의하는 설정들이 들어간다. 해당 설정 메소드의 모든 설정을 다루지는 못했다. 필자가 생각하기에 가장 많이 사용되는 부분의 설정만 다루었다.
- .userDetailsService(userDetailsService) : 사실 모든 사용목적은 살펴보지 못했지만, Refresh Token을 통해 Access Token을 재발급 받을 때 사용된다. UserDetailsService는 이전 Spring Security에서 다루었던 내용이므로 설명은 생략한다.
- .authorizationCodeServices(new JdbcAuthorizationCodeService(dataSource)) : 우리는 Authorization Code Grant Type으로 예제코드를 짜볼것이다. 해당 설정은 Resource Owner의 인증을 통하여 Client가 얻는 인증코드를 다루는 Service 클래스를 등록하는 설정이다. 여기서는 Jdbc를 이용한 AuthorizationCodeService를 사용하였다.
- .approvalStore(approvalStore()) : 만약 어떤 애플리케이션이 페이스북에서 나의 리소스를 사용한다고 가정하면, 최초에 페이스북에서 나의 리소스를 쓰도록 허락한 다음에는 더 이상 허락을 요구하는 메시지를 보여주지 않을 것이다. 그것은 어딘가에 내가 리소스사용을 허락한다라는 데이터가 저장되어 있기때문에 더 이상 물어보지 않는 것이다. 이것과 같이 Resource Owner가 Client 애플리케이션이 Resource Server에 있는 Resource Owner의 리소스의 사용을 허락한다는 데이터를 담는 approvalStore를 설정해주는 것이다.(DB에서 관리하기 위하여 JdbcApprovalStore를 사용하였다.)
- .tokenStore(tokenStore()) : 어떻게 보면 핵심이 되는 설정이다. 해당 설정은 TokenStore로써 어떤 것을 사용할 것인지를 설정하는 메소드이다. TokenStore의 종류로는 InMemoryTokenStore, JdbcTokenStore,JwtTokenStore,RedisTokenStore 등이 있지만, 우리는 JwtTokenStore를 사용할 것이다. JwtTokenStore를 빈으로 등록하였으며, JwtTokenStore 사용을 위한 JwtAccessTokenConverter를 빈으로 등록하였다.
맨 밑에 ClientRegistrationService 빈을 동적으로 클라이언트를 등록하기 위해 사용되는 서비스 클래스이다. 예를 들어 우리의 애플리케이션이 페이스북의 기능을 사용하기 위하여 사전에 App을 등록하는 과정이 있을 것이다. 거기에 사용되는 서비스 클래스라고 보면된다. 나중에 설명 할 것이다.
WebSecurityConfig.java
OAuth2.0과 Spring Security는 상호보완적이라고 얘기했다. 추후에는 어떻게 될지는 모르겠지만 현재는 그렇다. 다음 볼 코드는 시큐리티 관련 소스코드이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
|
/**
*
* @author yun-yeoseong
*
*/
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter{
@Autowired private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
/*
* AuthenticationProvider 등록
*/
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider());
}
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring()
.antMatchers("/resources/**")
.antMatchers("/css/**")
.antMatchers("/vendor/**")
.antMatchers("/js/**")
.antMatchers("/favicon*/**")
.antMatchers("/img/**")
;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.cors()
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login*/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf()
.disable()
.addFilter(authenticationFilter())
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint())
;
}
@Bean
public CorsConfigurationSource corsConfigurationSource() {
CorsConfiguration configuration = new CorsConfiguration();
configuration.setAllowedOrigins(Arrays.asList("*"));
configuration.setAllowedMethods(Arrays.asList("*"));
configuration.setAllowedHeaders(Arrays.asList("*"));
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", configuration);
return source;
}
/*
* SuccessHandler bean register
*/
@Bean
public AuthenticationSuccessHandler authenticationSuccessHandler() {
CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler successHandler = new CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler();
successHandler.setDefaultTargetUrl("/index");
return successHandler;
}
/*
* FailureHandler bean register
*/
@Bean
public AuthenticationFailureHandler authenticationFailureHandler() {
CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler failureHandler = new CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler();
failureHandler.setDefaultFailureUrl("/loginPage?error=error");
return failureHandler;
}
/*
* AuthenticationEntryPoint bean register
*/
@Bean
public AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint() {
return new CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint("/loginPage");
}
/*
* Form Login시 걸리는 Filter bean register
*/
@Bean
public CustomAuthenticationFilter authenticationFilter() throws Exception {
CustomAuthenticationFilter authenticationFilter = new CustomAuthenticationFilter(authenticationManager());
authenticationFilter.setFilterProcessesUrl("/login");
authenticationFilter.setUsernameParameter("username");
authenticationFilter.setPasswordParameter("password");
authenticationFilter.setAuthenticationSuccessHandler(authenticationSuccessHandler());
authenticationFilter.setAuthenticationFailureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler());
authenticationFilter.afterPropertiesSet();
return authenticationFilter;
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider() {
DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
authenticationProvider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);
authenticationProvider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
return authenticationProvider;
}
}
|
cs |
해당 설정은 이전 포스팅 Spring Security관련 글을 보면 조금더 자세히 설명하였다. 거기에서 참조하여 이해하면 될 것같다. 간단하게 설명하면 Authorization Server가 인증 코드를 발급해주기 위하여 Resource Owner에 대한 인증을 담당하게 될것이다. 그 밖에도 Authorization Server의 엔드포인트 보안이 필요하다면 여기에 작성하면 될것 같다.
다음은 OAuth2.0 및 Spring Security에 사용되는 클래스들이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
|
/*
* 동적으로 클라이언트를 등록할때 사용할 Client Type이다.
*/
public enum ClientType {
PUBLIC,CONFIDENTIAL
}
/**
*
* @author yun-yeoseong
* Spring Security에서 사용자의 Role(권한)이다.
*
*/
public enum UserRole {
ROLE_USER,
ROLE_ADMIN
}
/**
*
* @author yun-yeoseong
* View 랜더링을 위한 ViewController 설정이다.
*/
@Configuration
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{
/*
* ViewController
*/
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
WebMvcConfigurer.super.addViewControllers(registry);
registry.addViewController("/loginPage")
.setViewName("login");
}
}
/**
*
* @author yun-yeoseong
* Spring Security에서 사용자를 인증할때 사용되는 객체이다.(DB에서 관리되는 객체)
* UserDetailsService에서 사용자를 load할때 반환되는 결과객체이다.
*/
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@Entity
public class UserDetailsImpl implements UserDetails{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4608347932140057654L;
@Id
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private UserRole role;
@Column(length=2000)
private String access_token;
private LocalDateTime access_token_validity;
@Column(length=2000)
private String refresh_token;
@Transient
private Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities;
@Transient
private boolean accountNonExpired = true;
@Transient
private boolean accountNonLocked = true;
@Transient
private boolean credentialsNonExpired = true;
@Transient
private boolean enabled = true;
}
/*
* 동적클라이언트 등록시 컨트롤러에서 매개변수로 사용되는 Dto클래스.
*/
public class RegisterClientInfo {
private String name;
private String redirectUri;
private String clientType;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getRedirectUri() {
return redirectUri;
}
public void setRedirectUri(String redirectUri) {
this.redirectUri = redirectUri;
}
public String getClientType() {
return clientType;
}
public void setClientType(String clientType) {
this.clientType = clientType;
}
}
/*
* OAuth2.0에서 클라이언트 인증에 사용되는 객체이다.
* ClientDetailsService에서 load하면 반환하는 객체이다.
* Spring Security를 다루어보았다면, UserDetails와 동일한 역할을 하는 객체이다.
*/
public class ClientDetailsImpl extends BaseClientDetails {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8263549600098155096L;
private ClientType clientType;
public ClientType getClientType() {
return clientType;
}
public void setClientType(ClientType clientType) {
this.clientType = clientType;
}
}
/*
* Spring Security에서 로그인 페이지로 리다이렉트 시켜줄 Entrypoint객체이다.
* 만약 권한이 없는 사용자가 페이지에 접근하였을 때, 해당 객체가 로그인 페이지로
* 리다이렉트 시켜주는 역할을 담당한다.
*/
@Slf4j
public class CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint extends LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint{
public CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint(String loginFormUrl) {
super(loginFormUrl);
}
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("CustomAuthenticationEntryPoint.commence :::: {}",request.getRequestURI());
super.commence(request, response, authException);
}
}
/**
* 로그인 실패시 행동을 재정의할 클래스(추상 클래스가 아닌 인터페이스를 구현해도 된다.)
* Or Interface - AuthenticationFailureHandler
* @author yun-yeoseong
*
*/
@Slf4j
public class CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler extends SimpleUrlAuthenticationFailureHandler implements ExceptionProcessor{
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure ::::");
super.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, exception);
}
@Override
public void makeExceptionResponse(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Exception exception) {
}
}
/**
* Form 로그인 인증을 담당하는 Filter이다.
* @author yun-yeoseong
*
*/
@Slf4j
public class CustomAuthenticationFilter extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter{
private boolean postOnly = true;
public CustomAuthenticationFilter(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
super.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager);
}
/*
* 해당 필터에서 인증 프로세스 이전에 요청에서 사용자 정보를 가져와서
* Authentication 객체를 인증 프로세스 객체에게 전달하는 역할
*/
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
log.info("JwtAuthentication.attemptAuthentication ::::");
/*
* POST로 넘어왔는지 체크
*/
if(postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(username)) {
username = "";
}
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(password)) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}
/**
* 로그인 성공시 행동을 재정의할 클래스(추상 클래스가 아닌 인터페이스를 구현해도 된다.)
* Or Interface - AuthenticationSuccessHandler
* @author yun-yeoseong
*
*/
@Slf4j
public class CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler extends SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements ExceptionProcessor{
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws ServletException, IOException {
log.info("CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess ::::");
/*
* 쿠키에 인증 토큰을 넣어준다.
*/
super.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authentication);
}
@Override
public void makeExceptionResponse(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Exception exception) {
}
}
public interface ExceptionProcessor {
public void makeExceptionResponse(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Exception exception) throws IOException;
}
public interface ChatbotUserRepository extends JpaRepository<UserDetailsImpl, Long>{
public UserDetailsImpl findByUsername(String username);
}
public interface ChatbotUserService {
public UserDetailsImpl findByUsername(String username);
public UserDetailsImpl save(UserDetailsImpl user);
}
@Slf4j
@Service
public class ChatbotUserServiceImpl implements ChatbotUserService {
@Autowired private ChatbotUserRepository repository;
@Override
public UserDetailsImpl findByUsername(String username) {
log.info("ChatbotUserServiceImpl.findByUsername :::: {}",username);
return repository.findByUsername(username);
}
@Override
public UserDetailsImpl save(UserDetailsImpl user) {
log.info("ChatbotUserServiceImpl.save :::: {}",user.toString());
return repository.save(user);
}
}
/**
* Client 인증시 사용되는 서비스 클래스.
* DB에서 ClientDetails객체를 가져온다.
* Spring Security를 다루어보았다면 UserDetailsService와 동일한 역할을 한다.
* @author yun-yeoseong
*
*/
@Slf4j
@Primary
@Service
public class ClientDetailsServiceImpl extends JdbcClientDetailsService{
public ClientDetailsServiceImpl(DataSource dataSource) {
super(dataSource);
}
@Override
public ClientDetails loadClientByClientId(String clientId) throws ClientRegistrationException {
log.info("ClientDetailsServiceImpl.loadClientByClientId :::: {}",clientId);
return super.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
}
@Override
public void addClientDetails(ClientDetails clientDetails) throws ClientAlreadyExistsException {
log.info("ClientDetailsServiceImpl.addClientDetails :::: {}",clientDetails.toString());
super.addClientDetails(clientDetails);
}
@Override
public void updateClientDetails(ClientDetails clientDetails) throws NoSuchClientException {
log.info("ClientDetailsServiceImpl.updateClientDetails :::: {}",clientDetails.toString());
super.updateClientDetails(clientDetails);
}
@Override
public void updateClientSecret(String clientId, String secret) throws NoSuchClientException {
log.info("ClientDetailsServiceImpl.updateClientSecret :::: {},{}",clientId,secret);
super.updateClientSecret(clientId, secret);
}
@Override
public void removeClientDetails(String clientId) throws NoSuchClientException {
log.info("ClientDetailsServiceImpl.removeClientDetails :::: {}",clientId);
super.removeClientDetails(clientId);
}
@Override
public List<ClientDetails> listClientDetails() {
List<ClientDetails> list = super.listClientDetails();
log.info("ClientDetailsServiceImpl.listClientDetails :::: count = {}",list.size());
return list;
}
}
/*
* Spring Security에서 User를 인증할때 사용하는 서비스클래스이다.
* UserDetails 객체를 DB에서 가져오는 역할을 한다.
*/
@Slf4j
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService{
@Autowired private ChatbotUserService service;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
log.info("UserDetailsServiceImpl.loadUserByUsername :::: {}",username);
UserDetailsImpl user = service.findByUsername(username);
if(ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("Invalid username, please check user info !");
}
user.setAuthorities(AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList(String.valueOf(user.getRole())));
return user;
}
}
/*
* Sha256 암호화를 담당하는 유틸클래스.
*/
@Slf4j
public class Crypto {
public static String sha256(final String string) {
log.info("Crypto.sha256 :::: {}",string);
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
byte[] hash = digest.digest(string.getBytes("UTF-8"));
StringBuffer hexString = new StringBuffer();
for(int i=0;i<hash.length;i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & hash[i]);
if(hex.length() == 1) {
hexString.append('0');
}
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
/*
* 인증을 할때 Form에서 넘어온 비밀번호를 암호화하여
* DB에서 불러온 암호화된 인증패스워드를 비교하는 역할을 한다.
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class ShaPasswordEncoder implements PasswordEncoder{
@Override
public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) {
log.info("ShaPasswordEncoder.encode :::: {}",rawPassword);
return Crypto.sha256(rawPassword.toString());
}
@Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword) {
log.info("ShaPasswordEncoder.matches :::: {}<->{}",rawPassword,encodedPassword);
return Crypto.sha256(rawPassword.toString()).equals(encodedPassword);
}
}
|
cs |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
/*
* 동적 클라이언트 등록에 사용되는 컨트롤러
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/client")
public class ClientController {
@Autowired private ClientRegistrationService clientRegistrationService;
@GetMapping("/register")
public ModelAndView registerPage(ModelAndView mav) {
mav.setViewName("client/register");
mav.addObject("registry", new RegisterClientInfo());
return mav;
}
@GetMapping("/dashboard")
public ModelAndView dashboard(ModelAndView mv) {
mv.addObject("applications",
clientRegistrationService.listClientDetails());
return mv;
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public ModelAndView save(@Valid RegisterClientInfo clientDetails,ModelAndView mav ,BindingResult bindingResult) {
if(bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
return new ModelAndView("client/register");
}
ClientDetailsImpl client = new ClientDetailsImpl();
client.addAdditionalInformation("name", clientDetails.getName());
client.setRegisteredRedirectUri(new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList("http://localhost:9000/callback")));
client.setClientType(ClientType.PUBLIC);
client.setClientId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
client.setClientSecret(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
client.setAccessTokenValiditySeconds(3600);
client.setScope(Arrays.asList("read","write"));
clientRegistrationService.addClientDetails(client);
mav.setViewName("redirect:/client/dashboard");
return mav;
}
@GetMapping("/remove")
public ModelAndView remove(
@RequestParam(value = "client_id", required = false) String clientId) {
clientRegistrationService.removeClientDetails(clientId);
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView("redirect:/client/dashboard");
mv.addObject("applications",
clientRegistrationService.listClientDetails());
return mv;
}
}
|
cs |
클래스설명(대부분 소스 주석에 간단히 달아놓았다.)
- ClientType : 클라이언트 동적등록에 사용되는 이늄. 인증 서버에 등록할 클라이언트 애플리케이션의 타입이다.
- UserRole : Resource Owner의 Role 이늄.(Spring Security에서 사용될 권한 타입이다.)
- WebMvcConfig : MVC 설정을 위한 클래스.
- ClientDetailsImpl : ClientDetails를 구현한 BaseClientDeatils를 상속한 클래스이다. Client 인증에 사용될 클래스이다. ClientDetailsService와 상호보완적인 클래스이다.(Spring Security의 UserDetails 와 비슷한 역할이다. 주체가 사용자에서 클라이언트 애플리케이션으로 갔다고 보면된다.)
- RegisterClientInfo : 클라이언트 동적 등록에 사용될 Controller Dto 클래스.
- UserDetails : Resource Owner의 인증에 사용되는 클래스. UserDetailsService와 상호보완적이다.
- ChatbotUserRepository : UserDetailsImpl JPA Repository 인터페이스이다.
- ClientDetailsServiceImpl : 클라이언트 인증에 사용되는 서비스 클래스이다. 인증 과정에서 DB에서 사용자 정보를 가져오는데 사용된다.
- UserDetailsServiceImpl : 위와 동일한 역할이며 인증 주체가 Resource Owner이다.
- Crypto,ShaPasswordEncoder : 비밀번호 암호화에 사용되는 클래스들이다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
INSERT INTO oauth_client_details
(client_id, resource_ids, client_secret, scope, authorized_grant_types,
web_server_redirect_uri, authorities, access_token_validity, refresh_token_validity,
additional_information, autoapprove)
VALUES
('clientapp', null, '311ffdc998038e85ac0b5bd1fb20097a67281b7c0bc0ef905771daec9eb52b66',
'read_profile,read_posts', 'authorization_code,refresh_token',
'http://localhost:9000/callback',
null, 3000, -1, null, 'false');
INSERT INTO USER_DETAILS_IMPL values('1','5e884898da28047151d0e56f8dc6292773603d0d6aabbdd62a11ef721d1542d8','ROLE_USER','ResourceOwner');
commit;
|
cs |
예제를 진행하기 위하여 위의 2개의 데이터를 DB에 넣어준다. Resource Owner의 패스워드는 물론 Client Secret도 암호화가 되어 들어가있다는 점을 유의해야한다. 현재는 PasswordEncoder가 빈으로 떠있음으로 암호화가된 형태로 DB에 데이터가 들어가야한다. 혹은 http://localhost:8080/register에 접속하여 동적으로 클라이언트를 등록하여도 된다. 하지만 Resource Owner는 수동으로 등록해주어야한다.
브라우저를 킨다. 그리고 아래 Url로 접근을 시도해보자. 해당 Url은 Authorization Code를 받기 위한 Url 요청이다.
쿼리스트링들에 뭐가 담겨있는지 꼭 확인하자. client_id을 명시해주고, 인증코드를 받기위한 redirect_uri를 명시하고, 해당 요청을 인증코드를 받기위한 요청이므로 response_type을 code로 명시하고 해당 client의 scope를 작성한다. 그리고 마지막으로 cors를 위하여 state 코드를 임의로 넣어준다.

만약 예제를 잘 따라왔다면 로그인 페이지로 리다이렉트 될것이다. 로그인 해주자.

만약 로그인에 성공하였다면 Resource Owner에게 Client가 자신의 리소스를 사용하기 위해 Resource Server에 접근하는 것을 허락할 것인가를 물어보는 페이지를 보여준다. Approve를 클릭하고 인증버튼을 누르자.
http://localhost:9000/callback?code=s470jJ&state=xyz 이렇게 인증코드가 위에 쿼리스트링에 등록한 Redirect_uri로 전달된 것을 볼 수있다. 여기하나 중요한 것이있다. DB에 넣은 Redirect_uri와 authorize요청에 포함시킨 Redirect_uri가 다르다면 토큰은 물론 인증코드 조차 받을 수 없다. 내부적으로 DB와 쿼리스트링의 Redirect_uri를 비교하여 동일한지 판단하기 때문이다. 받은 인증코드로 토큰을 요청해보자.

필자는 Postman 툴을 이용하여 토큰발급 요청을 보내보았다. 우선 화면에서 보이지 않은 Headers 설정이다.
"Content-Type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded" 컨텐츠 타입은 urlencoding을 해서 보낸다.
clientapp:db637df2-338b-4aaf-b609-eb60676834dc@localhost:8080/oauth/token?code=s470jJ&grant_type=authorization_code&scope=read_profile&redirect_uri=http://localhost:9000/callback
Url이다. Basic Authentication에 클라이언트 아이디와 Secret을 넣어준다. 그리고 받은 인증코드와 그랜트 타입, 스코프, 리다이렉트 Uri를 쿼리스트링으로 넣어준다. 결과를 보면 access_token,token_type,refresh_token,expires_in,scope,jti가 결과값으로 온것을 볼 수 있다. 이후 클라이언트는 헤더에 아래 내용을 포함하여 요청을 보내면 Resource Server에 보호되고 있는 리소스 요청을 보낼 수 있게된다.
Header : Authorization Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJleHAiOjE1NTYzODYwNjQsInVzZXJfbmFtZSI6IjEyMjN5eXMiLCJhdXRob3JpdGllcyI6WyJST0xFX1VTRVIiXSwianRpIjoiNmQ5ZmM5ZTUtZDk3OC00NmVhLThiYjktOTFiZDY5ZThjZTc4IiwiY2xpZW50X2lkIjoiY2xpZW50YXBwIiwic2NvcGUiOlsicmVhZF9wcm9maWxlIl19.WnB9EVQ76gfuLnmqplcZwbJLMYnVO2rblo6AST5gso8
혹시 Jwt 토큰에 대해 잘 알지 못한다면 아래 링크를 참조하자.
https://coding-start.tistory.com/157?category=738633
Algorithm - JWT 위변조를 알아내는 HMAC이란?
오늘 포스팅할 내용은 HMAC에 대한 설명이다. 우선 HMAC에 대해 설명하기 이전에 요즘 대부분이 사용하고 있는 토큰인증 방식에 이용되는 JWT(Json Web Token)이다. 그렇다면 JWT란 무엇일까? JSON Web Token은..
coding-start.tistory.com
오늘은 여기까지 Authorization Server 설정까지 하였다. 굉장히 범위가 넓은 주제이기도 하므로, 나머지 동적 클라이언트 등록 및 Resource Server와 Client 애플리케이션은 다음 포스팅에서 다루어볼 것이다. 성의없는 글을 보느라 고생하셨을 것이라 생각한다 다음 포스팅은 조금더 친절하게..
<깃헙 주소>
yoonyeoseong/spring-oauth2.0
Contribute to yoonyeoseong/spring-oauth2.0 development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com